The Essential Guide to Server Hardware

In the realm of modern technology, the backbone of data management and storage lies in robust and efficient server hardware. From small businesses to large enterprises, understanding the components and capabilities of computer server hardware is crucial for optimal performance and reliability. This guide delves into the intricacies of server hardware, exploring its components, functions, and the significant role it plays in today’s digital landscape.
What is Server Hardware?
Server hardware refers to the physical components that constitute a server. Unlike standard desktop computers, servers are designed to manage, store, and process data for multiple users and applications. They are engineered for high performance, reliability, and scalability to meet the demands of various computing environments. The primary purpose of server hardware is to support network resources, run applications, and provide data services across an organization.
Key Components of Server Hardware
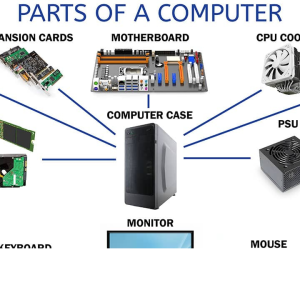
- Motherboard: The motherboard is the central hub that connects all the components of the server. It houses the CPU, RAM, and other essential hardware, providing communication pathways between them. Server motherboards are designed to support multiple CPUs, large amounts of RAM, and additional features like advanced network interfaces and storage options.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Often referred to as the brain of the server, the CPU executes instructions and processes data. Servers typically use multi-core processors to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, ensuring efficient data processing and application performance. High-end servers may utilize multiple CPUs to enhance processing power further.
- Memory (RAM): Random Access Memory (RAM) is critical for a server’s performance, as it temporarily stores data that the CPU needs to access quickly. Servers often require substantial amounts of RAM to manage large datasets and support numerous applications running concurrently. ECC (Error-Correcting Code) RAM is commonly used in servers to detect and correct data corruption, ensuring data integrity.
- Storage: Server storage solutions range from traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) to solid-state drives (SSDs). HDDs offer high capacity at a lower cost, while SSDs provide faster data access speeds and improved reliability. Servers may also use RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations to enhance performance and data redundancy.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): A reliable PSU is essential for server stability. Servers often use redundant power supplies to ensure continuous operation in case one unit fails. Efficient power supplies also contribute to lower energy consumption and reduced operating costs.
- Network Interface Card (NIC): The NIC enables the server to communicate with other devices on the network. High-speed network interfaces, such as 10 Gigabit Ethernet or even faster options, are crucial for handling large volumes of data transfer and ensuring minimal latency.
- Cooling Systems: Servers generate significant heat during operation, making effective cooling systems vital. Advanced cooling solutions, including heat sinks, fans, and liquid cooling, help maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent hardware damage.
- Chassis: The server chassis, or case, houses all the components and provides physical protection. It is designed for efficient airflow and easy maintenance. Rack-mounted chassis are common in data centers, allowing for efficient use of space and easy scalability.
The Importance of Server Hardware in Business Operations
Investing in quality server hardware is essential for businesses aiming to ensure seamless operations and robust data management. Here are some key reasons why server hardware is crucial:
- Performance: High-quality server hardware delivers superior performance, enabling faster data processing and efficient application management. This results in improved productivity and user experience.
- Reliability: Server hardware is built for continuous operation, offering higher reliability compared to consumer-grade components. Features like ECC RAM, redundant power supplies, and RAID configurations contribute to system stability and data integrity.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, their data processing and storage needs expand. Server hardware provides scalability options, allowing organizations to add more resources without significant infrastructure changes.
- Security: Servers often host sensitive data and critical applications. Advanced server hardware includes security features such as hardware encryption, secure boot, and Trusted Platform Module (TPM) to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Cost Efficiency: While the initial investment in server hardware can be substantial, the long-term benefits include reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, and improved energy efficiency. This translates to cost savings over time.
Choosing the Right Server Hardware
Selecting the appropriate server hardware depends on several factors, including the specific needs of the organization, budget constraints, and future growth projections. Here are some considerations:
- Workload Requirements: Determine the type of applications and workloads the server will handle. For instance, a server used for database management will have different hardware requirements compared to a server running virtual machines.
- Performance Needs: Assess the performance demands, such as CPU processing power, memory capacity, and storage speed. High-performance servers are essential for resource-intensive tasks and large-scale operations.
- Reliability and Redundancy: Consider hardware features that enhance reliability, such as redundant power supplies, ECC RAM, and RAID configurations. These features minimize the risk of hardware failure and data loss.
- Scalability Options: Ensure the server hardware supports future expansion. This includes additional RAM slots, CPU sockets, and storage bays, allowing for easy upgrades as business needs evolve.
- Energy Efficiency: Opt for energy-efficient hardware to reduce operational costs and minimize the environmental impact. Look for components with high-efficiency ratings and advanced power management features.
- Vendor Support and Warranty: Choose reputable vendors that offer comprehensive support and warranty options. Reliable customer support and extended warranties provide peace of mind and ensure timely resolution of hardware issues.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of server hardware is vital for businesses aiming to optimize their IT infrastructure. From selecting the right components to ensuring reliable performance and scalability, investing in quality server hardware is a strategic decision that drives operational efficiency and long-term success. By carefully evaluating workload requirements, performance needs, and scalability options, organizations can build robust server environments that support their growth and technological advancements.
If you have any questions for us, you can see more at: https://hardwarepc.xyz/, X